
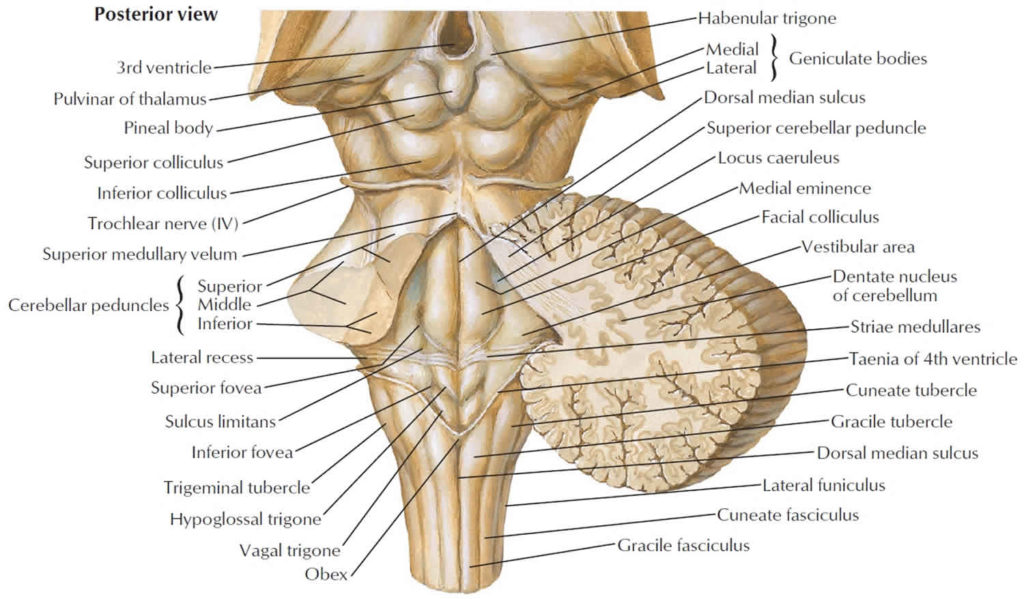
While these patients look awake and often alert they have no discernible meaningful interaction with their environment. Persistent vegetative state refers to this condition in its permanent form and designates patients who survive for prolonged periods (sometimes years) following a severe brain injury without ever recovering any outward manifestations of higher mental activity. subcortical) regions of the brain, without activity of the cerebral cortex itself. The vegetative state is produced by intact function of the brain stem and “deeper” (i.e.

sucking, startle responses, grabbing), accompanied by a total lack of cognitive or mental activity of any type. eye opening), sleep-wake cycles, and reflex movements (e.g. It comprises a return of wakefulness (e.g. Persistent vegetative state describes the chronic condition that almost invariably emerges after coma. Patients in coma will have these signs patients who suffer brain death will not. The physician(s) observes the patient for any sign of electrical impulse leaving the brain as a result of an external stimulus. The amount of brain activity is variable, and extensive clinical examinations are performed on these patients. Patients who are in coma will have some neurological signs. In either case, the patient is considered legally alive. The individual in the vegetative state has a lot more lower-brain function, and a bit more upper brain-stem function, than a patient in deep coma. The difference between these two groups is that a deep coma patient usually requires hospital care, while a patient in a vegetative state may be released to the family for home care. drug overdose, lack of oxygen).įind out about the SUPERNOVA study for the prevention of COVID-19 in people with an impaired immune system trauma, bleeding, stroke), or (2) toxic/metabolic (e.g. All causes of coma can be divided into two main categories: (1) structural (e.g. No matter how much the patient is stimulated, he or she is incapable of becoming fully alert.Īny serious injury to both cerebral hemispheres or the brain stem can produce coma. By contrast, coma is characterized by slowing and depression of electrical brain activity, and implies a neurologic deficit. With stimulation, a sleeping person can be quickly aroused to a state of complete alertness. Sleep is characterized by highly organized and complex electrical brain activity, and can easily be reversed. Coma outwardly resembles sleep, but is physiologically very different. This means absence of spontaneous respiration in response to a hypercarbic stimulus.Ĭoma refers to a state of general “brain failure” characterized by severe depression of level of consciousness. This includes unreactive pupils, the absence of ocular responses, facial sensation and motor responses, and lack of cough and gag reflexes.ģ. MUST READ: “Brain Dead” Child Showing Signs Of Lifeĩ Ways to Protect Yourself from Breathing Wildfire SmokeĢ. This hormone is produced to concentrate the urine in the kidneys, thus protecting against life-threatening dehydration. A good example is the brain’s production of anti-diuretic hormone (ADH). The brain also produces hormones to control individual organ function. These functions include auditory, olfactory, visual and tactile senses, regulation of body temperature, blood pressure, respiration, and heart rate (although the heart can continue to beat without the brain in “autotonic response”). The brain controls not only an individual’s thought process and voluntary movements, but it controls involuntary movements and other vital body functions. The brain has a number of vast jobs to complete every second and is a very complex organ.
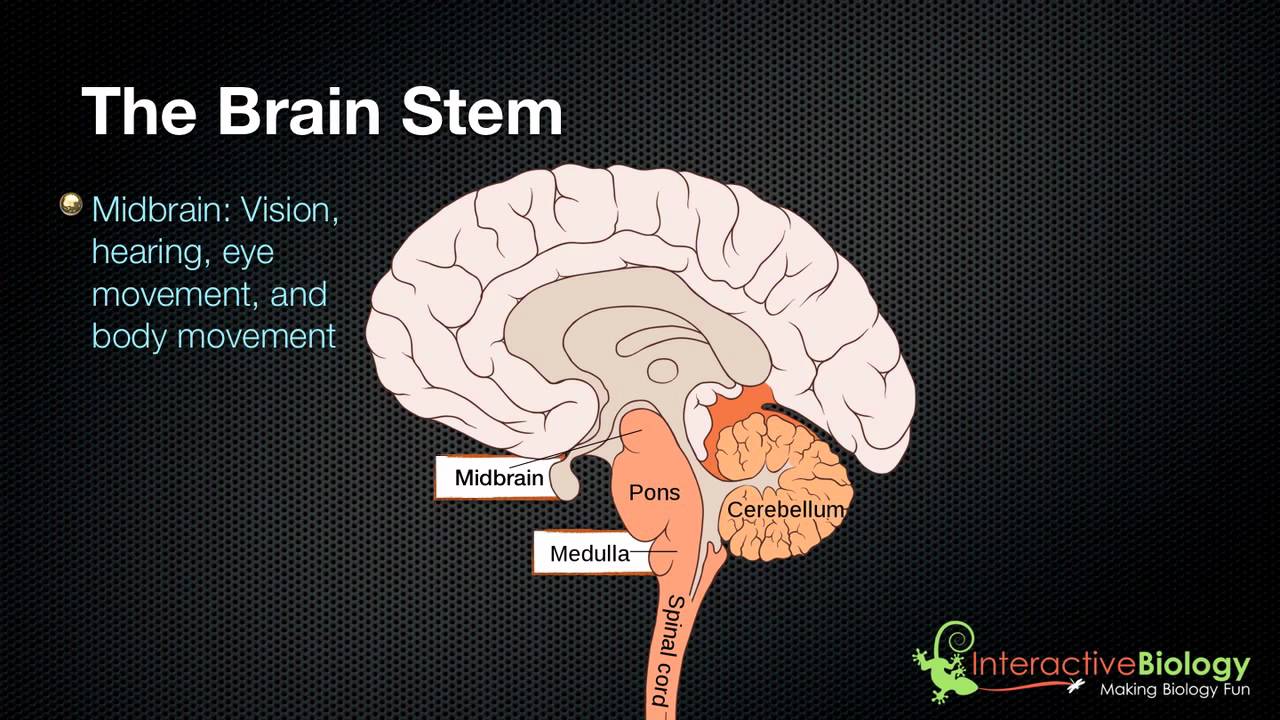
And patients who are in coma may or may not progress to brain death. First things first, patients who suffer brain death are not in coma. In light of Whitney Houston and Bobby Brown’s daughter, Bobbi Kristina being found unconscious, there have been many headlines that said she in “a coma” or a “vegetative state” or even “brain dead”.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
